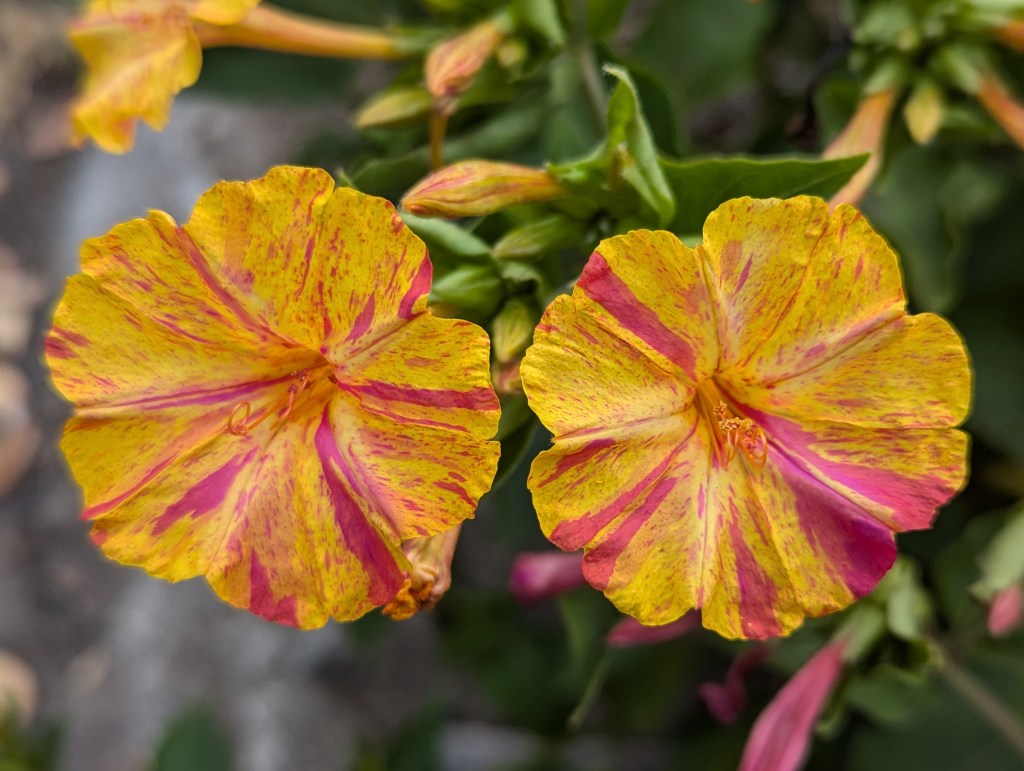
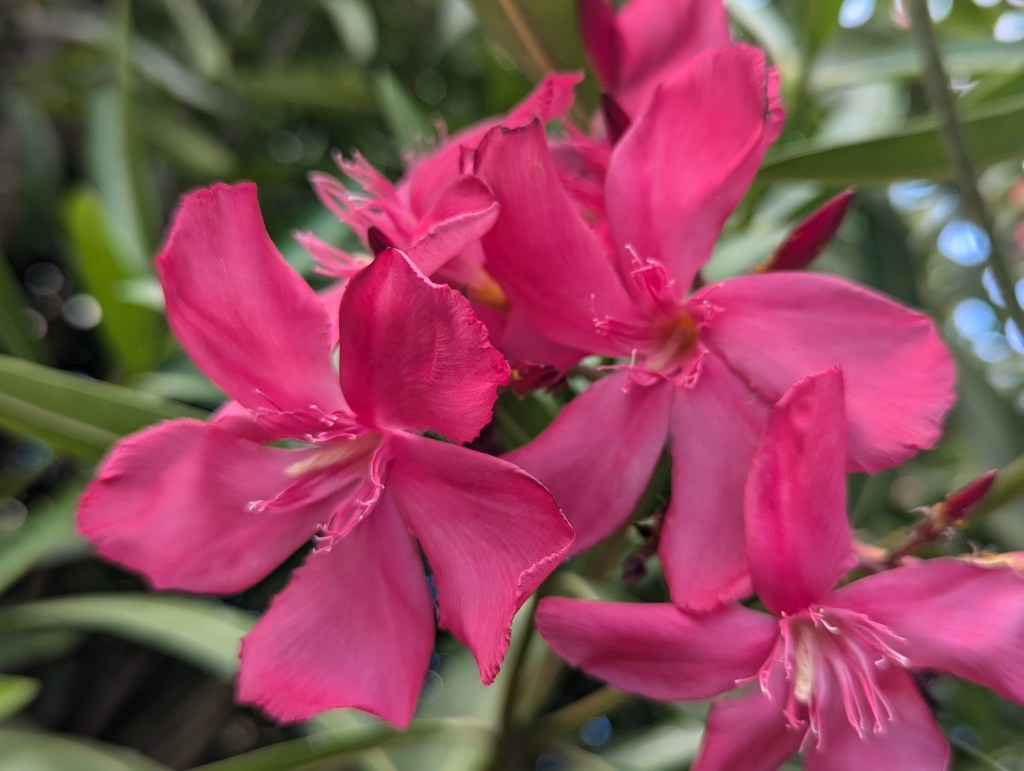
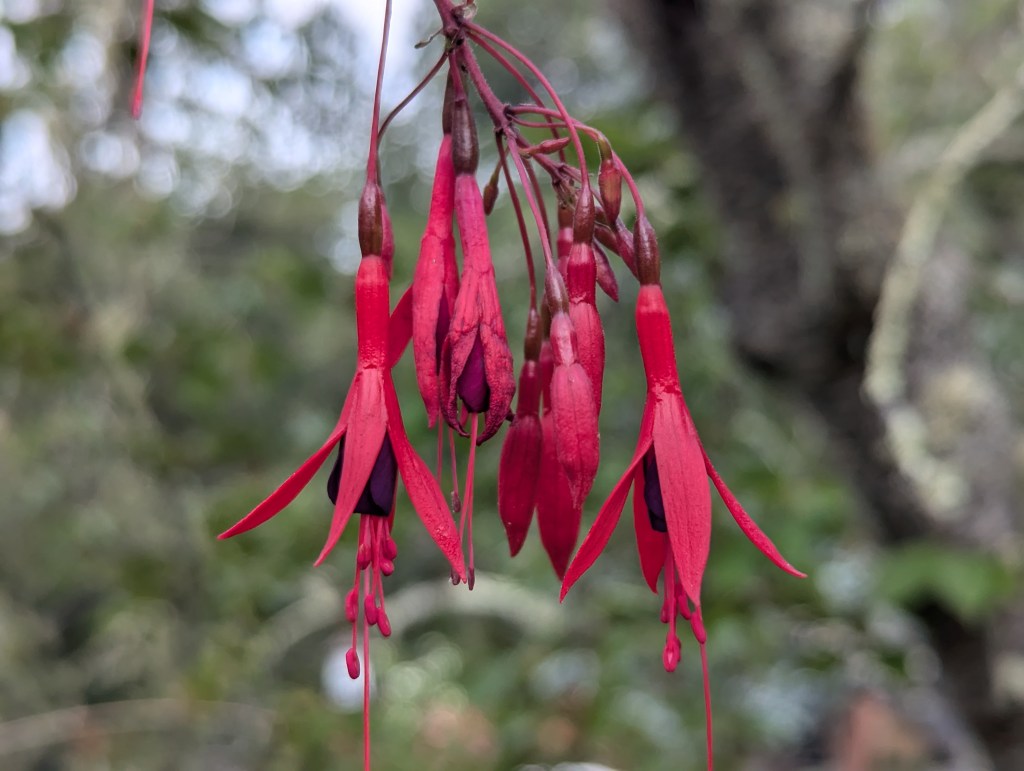
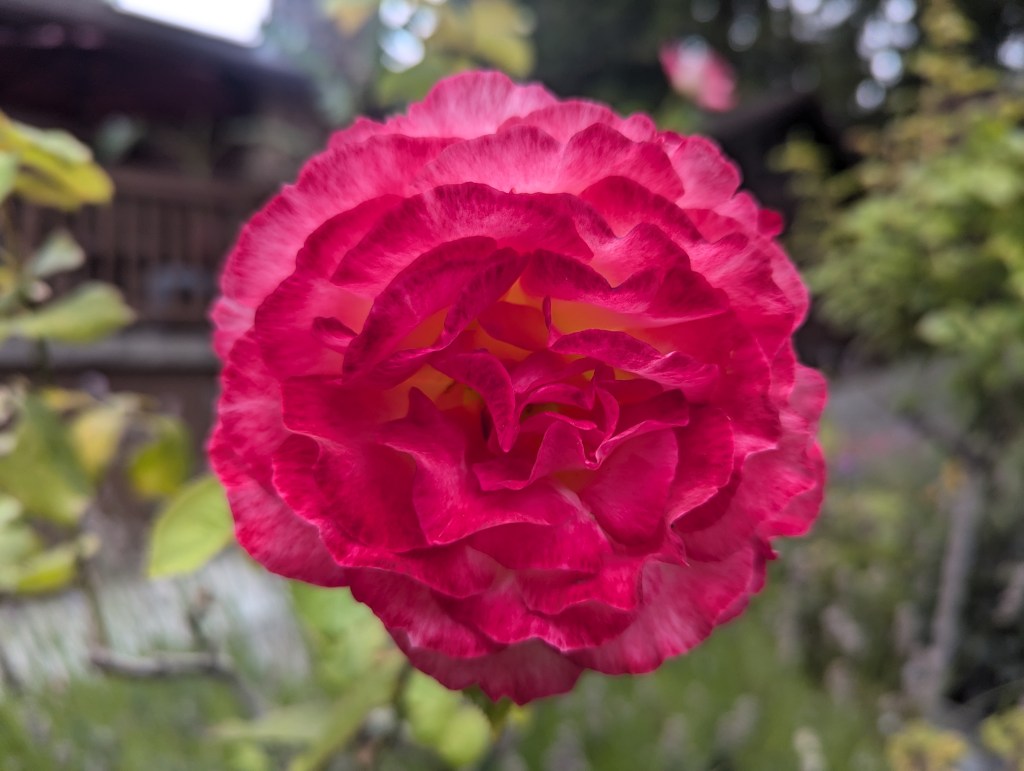
Feral flowers are technically not the same as wildflowers. As their designation suggests, wildflowers grow wild. They always have, without intervention. They are naturally native. Their native ranges can fluctuate, but do so naturally as associated ecosystems change. Their status as wildflowers does not change within home gardens or refined landscapes.
Feral flowers are progeny of cultivated flowers. Almost all are exotic, or nonnative. Some are true to type, which means that they are indistinguishable from the originals. However, because of extensive breeding, many revert to a more genetically stable state. Some can naturalize, or perpetuate without intervention. Then, they seem to behave as wildflowers.
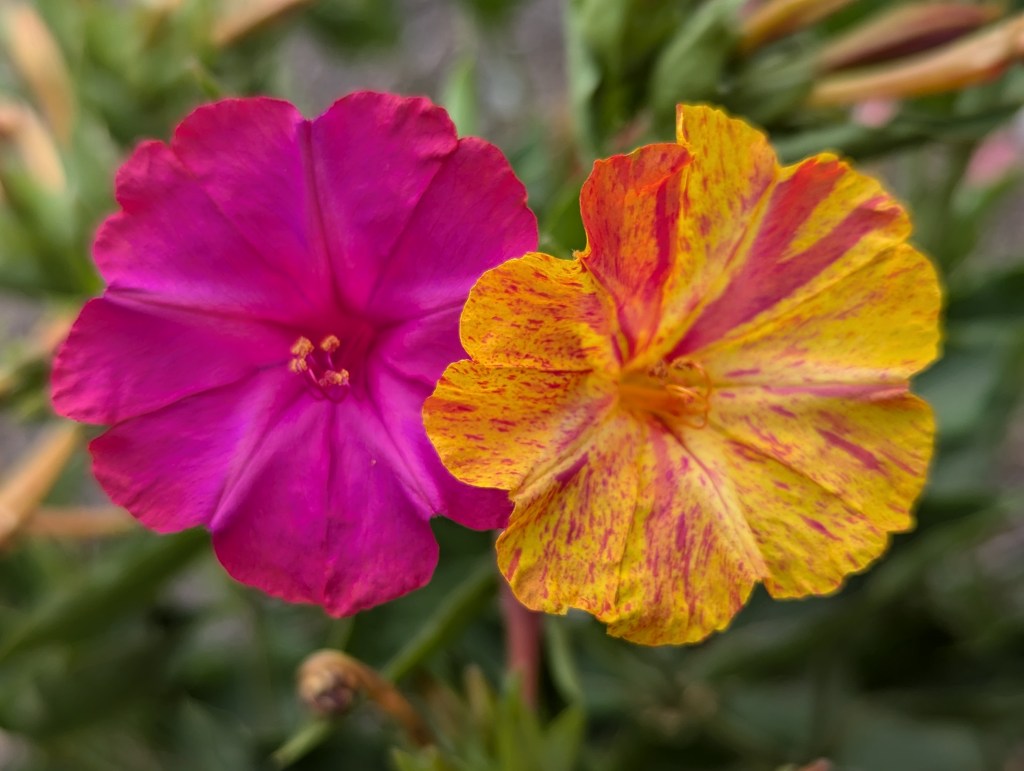
For example, most home garden nasturtiums begin as garden varieties. They bloom with particular colors because of their breeding and selection. Their progeny, however, bloom with more natural floral color. After a few generations, they may bloom only basic orange and yellow. Such feral flowers can naturalize within riparian ecosystems like wildflowers.
Because they are not native, naturalized nasturtium are technically not wildflowers. They are merely naturalized feral flowers. Although they are rarely aggressively invasive, they can interfere with natural ecology. They might compete with native species for resources and space. They can sustain organisms that are pathogens to native vegetation species.
California poppy is a genuinely native wildflower. However, a few home garden varieties developed from selection and breeding. Initially, such varieties bloom with unusual floral colors like white, lavender, pink or red. After a few generations, though, their colors revert to their more natural orange. Although wildflowers, they are also technically feral flowers.
Many of the most noxious weeds here escaped from home gardens and naturalized. For example, common pink pampas grass became popular during the Victorian Period. Now, it is quite naturalized and compromising ecosystems throughout the West Coast. Its feral flowers are appealing, but perpetuate infestation. They are surely not native wildflowers. Water hyacinth and yellow flag are other examples.